Executive Summary
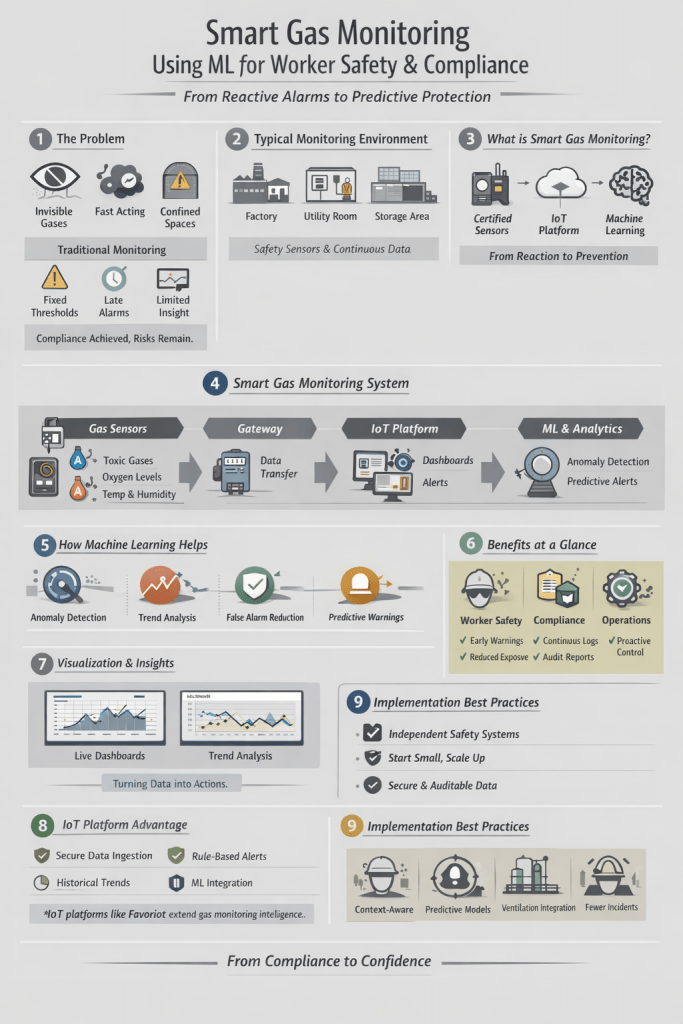
Many industrial workplaces expose workers to hazardous gases that are invisible and difficult to detect without proper instrumentation. Even short exposure beyond safe limits can cause serious injury or long-term health issues. Traditional gas monitoring systems rely mainly on threshold alarms that activate only when conditions become dangerous. While this approach supports compliance, it offers limited help in preventing incidents.
Smart gas monitoring combines safety-grade gas sensors, continuous data collection, and machine learning techniques to strengthen worker protection and compliance. By learning patterns and trends instead of reacting only to fixed limits, organisations gain earlier warnings, clearer insight, and better control through a cloud-based IoT platform.
Why Gas Monitoring Remains a Safety Challenge
Industrial gas hazards are difficult to manage because they are:
- Intermittent and location-dependent
- Influenced by ventilation, temperature, humidity, and work activity
- Dangerous even at relatively low concentrations
- Especially critical in confined or enclosed spaces
Common limitations of conventional gas monitoring include:
- Alarms are triggered only after limits are exceeded
- Minimal use of historical data
- Repeated alarms without a clear root cause
- Nuisance alerts that reduce worker trust
Meeting regulatory limits alone does not always translate into safer operations.
A Typical Smart Gas Monitoring Scenario
In a typical facility such as a factory, processing plant, or utility site, fixed gas sensors are installed across key areas, including:
- Production and processing zones
- Utility and equipment rooms
- Storage and loading areas
- Confined or enclosed spaces
These sensors continuously measure hazardous gas concentrations and support environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. The sensors are calibrated for occupational use and generate time-stamped data that reflects both routine operations and abnormal situations.
System Architecture Overview
A smart gas monitoring solution typically follows a layered approach:
- Gas sensors continuously capture readings
- A gateway aggregates data and handles secure transmission
- A cloud IoT platform stores and visualises information
- An analytics layer applies rules and machine learning models
- Alerts, dashboards, and reports support timely decisions
This structure allows safety-critical detection to remain independent while enabling higher-level insight and analysis.
How Machine Learning Enhances Gas Monitoring
Machine learning shifts gas monitoring from simple limit checking to behavioural understanding.
Instead of asking:
- “Has the threshold been exceeded?”
The system can ask:
- “Is this behaviour unusual for this location and time?”
Key ML-driven capabilities include:
- Anomaly detection
Identifies unusual gas patterns even when readings remain within safe ranges - Trend analysis
Highlights gradual increases that may signal leaks, ventilation issues, or process degradation - Reduced false alarms
Distinguishes short-term spikes from genuine risks - Predictive alerts
Estimates the likelihood of a future alarm based on current trends
These capabilities allow safety teams to act earlier and with greater confidence.
Benefits for Safety, Compliance, and Operations
A smart gas monitoring approach delivers value across several areas.
For worker safety:
- Earlier warnings reduce exposure risk
- Better visibility across zones and shifts
- Improved readiness for confined space work
For compliance:
- Continuous, auditable gas exposure records
- Easier preparation for inspections and audits
- Clear evidence of proactive risk management
For operations:
- Root cause analysis of recurring incidents
- Insight into ventilation and process performance
- Data-supported improvements rather than guesswork
Visualisation and Decision Support
Modern IoT platforms turn raw sensor readings into practical insight through:
- Real-time dashboards by zone and gas type
- Historical charts for exposure and trend review
- Alert timelines linked to operational activity
Platforms such as Favoriot provide a practical environment for ingesting sensor data via common protocols, configuring rule-based alerts, visualising trends, and supporting machine learning workflows. This allows organisations to begin monitoring and progressively introduce predictive insights without replacing existing safety-certified equipment.
Teams that already operate gas sensors can consider connecting selected data streams to an IoT platform to gain visibility, historical insights, and early-warning capabilities with minimal disruption.
Key Implementation Considerations
Successful deployment depends on a few important principles:
- Clear separation of roles
Safety-certified sensors handle detection and alarms, while the IoT and ML layer focuses on insight and prediction - Scalable rollout
Begin with high-risk areas, then expand coverage as data volume and confidence grow - Data security and integrity
Secure communication, access control, and audit trails are essential for trust
This approach supports progress without introducing compliance risk.
The Road Ahead
Smart gas monitoring is evolving toward systems that are:
- Context-aware and adaptive
- Integrated with ventilation and facility systems
- Linked to maintenance and operational planning
- Increasingly predictive as data accumulates
As machine learning models mature, safety teams can prevent incidents rather than respond after they occur.
Conclusion
Gas monitoring no longer needs to stop at alarms. By combining safety-grade sensors, continuous data collection, and machine learning, organisations can protect workers more effectively while strengthening compliance and operational understanding.
A cloud-based IoT platform with analytics and ML capability offers a practical path toward proactive safety. Organisations looking to move beyond basic monitoring may consider connecting their gas monitoring systems to platforms such as Favoriot to gain deeper insight, earlier warnings, and a stronger foundation for intelligent safety management.